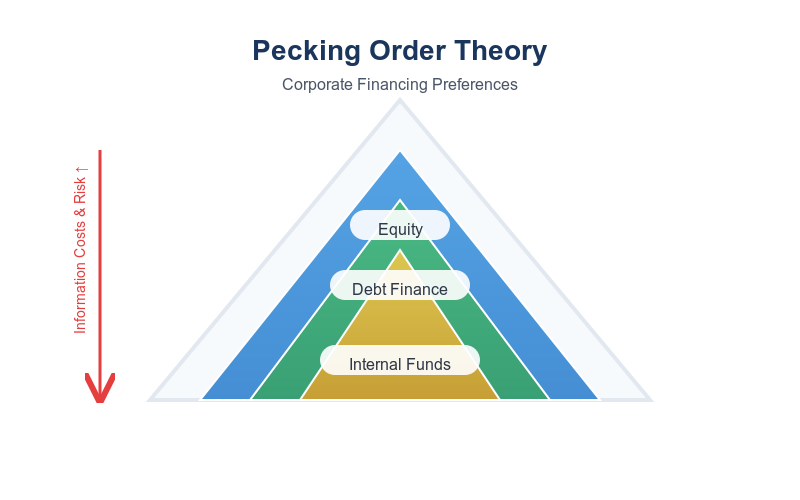
The pecking order theory is a concept in corporate finance that suggests that firms have a preferred hierarchy, or “pecking order,” for financing their investments and capital expenditures. This theory explains that firms prefer to fund investments using internal financing sources first, followed by debt financing, and finally resorting to issuing equity as a last resort.
Principles of Pecking Order Theory:
Internal Financing/(Retained Earning)
According to the pecking order theory, firms prefer to fund investments using internal sources of funds, such as retained earnings or cash flows generated from operations. Internal financing is considered the most preferred option because it does not entail any costs or dilution of ownership.
Debt Financing
If internal financing sources are insufficient to fund investments, firms may turn to debt financing as the next best option. Debt financing allows firms to leverage their existing assets and cash flows by borrowing funds from external sources, such as banks,or other lenders. Debt financing is considered less costly than equity financing because interest payments are tax-deductible, and debt holders have a fixed claim on the company’s assets and cash flows.
Equity Financing
Equity financing, such as issuing new shares of common stock, is considered the least preferred option according to the pecking order theory. Equity financing entails diluting existing shareholders’ ownership stakes and may signal to investors that the firm’s stock is undervalued. Additionally, issuing equity may involve transaction costs, such as underwriting fees and issuance expenses, which can reduce the net proceeds received by the firm.
Information Asymmetry
The pecking order theory is based on the assumption of asymmetric information between managers and investors. According to the theory, managers possess better information about the firm’s financial condition and investment opportunities than outside investors. As a result, managers may be reluctant to issue equity if they believe the stock is undervalued or if they are concerned about adverse selection effects.
Read more on Wiki